The number of new COVID-19 infections in rural America dropped slightly last week but remained at near-record numbers as the nation heads into the holiday weekend.
New infections in rural counties numbered 204,960 last week, a 7 percent drop from the previous week’s record-setting 220,554 cases.
COVID-related deaths also dropped marginally in nonmetropolitan counties last week, with 3,754 deaths reported. That’s down 2 percent from the previous week’s record-setting 3,818 deaths.
This week’s Daily Yonder coronavirus update covers Sunday, December 13, through Saturday, December 19. Data is from the nonprofit USA Facts.
- After months of spreading more quickly in rural areas than in urban ones, the rate of new infections in rural and urban areas was nearly equal last week. (See graph above.)
- The rate of new deaths remained substantially higher in rural areas, however. (See graph above.)
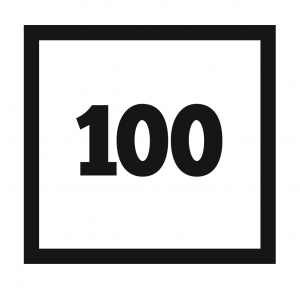
- Last week 95 percent of all U.S. counties – urban and rural – were in the red zone, defined as having a rate of 100 or more new infections per 100,000 residents. The White House Coronavirus Task Force says localities in the red zone need to take additional measures to control the virus.
- The number of counties with very high rates of new infections (defined as more than 500 new infections per 100,000 in a week) declined last week. The number of rural counties in the very-high category (shown in black on the map above) dropped from 391 two weeks ago to 326 last week.
- The number of urban counties in the very-high category (shown in gray in the map above) declined to 637 from 767.
- Pockets of very high infection rates were visible in Tennessee, Arizona, Southern California and the Great Lakes states from Illinois to Pennsylvania.
- Tennessee had the nation’s highest rural new-infection rate last week, 970 new infections per 100,000 residents. That means nearly 1 percent of the state’s rural population contracted COVID-19 last week, according to state health department reports. Metropolitan areas had a rate of 765 per 100,000. These rates were calculated using only six days of data for the week because reporting was late on Saturday. Tennessee had nearly 6,000 additional infections that day, but the numbers were not part of USA Facts’ reporting for the week.
- Of states with rural counties, Tennessee had the highest percent of counties in the very-high infection-rate category (black and gray in the map above). Ninety-four of the state’s 95 counties had new infection rates in the very-high range.
- Arizona had 13 of 15 counties with very high rates.
- Other states with more than half of their counties with very-high infection for the week were Indiana (71 of 92 counties), Oklahoma (58 of 77), Pennsylvania (49 of 67), Ohio (59 of 88), Alabama (43 of 67), Arkansas (44 of 75), Kansas (55 of 105), Illinois (53 of 102) and Utah (15 of 29).
This article was originally published by the Daily Yonder.